Press release
Wide variation in the risk of side effects after COVID-19 vaccination
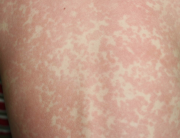
Some people who received Pfizer/BioNTech’s COVID-19 vaccine had a significantly higher risk of reported side effects than others.
This is the main finding of a research collaboration that has analysed data from Sweden and
Denmark, published in the journal Medicina (https://www.mdpi.com/1648-9144/60/8/1343)
Using official records, the researchers identified the same worrying trends in Swedish data that they had found in a previous study of Danish data.
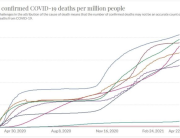
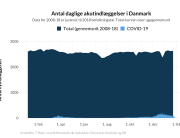
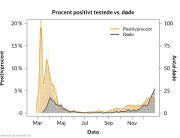
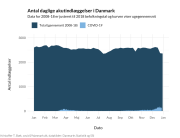
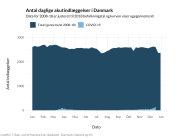
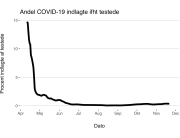
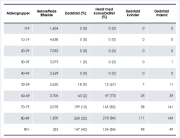
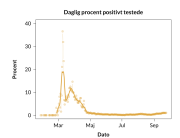
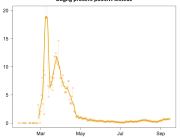
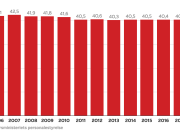
COVID-19 vaccine administered during the first months of the vaccination roll out resulted in significantly more side effects. It was mainly the elderly, care workers and other healthcare professionals who received these early batches.
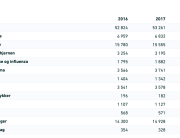
Seeking to confirm their earlier findings (Schmeling et al., 2023) in an independent data set, the researchers analysed publicly available records of suspected adverse events related to BNT162b2/Comirnaty from the Swedish Medical Products Agency (57,000 records spanning 3 years of reports).
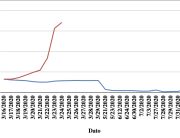
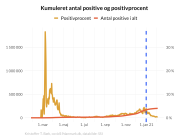
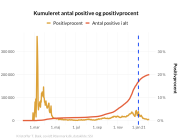
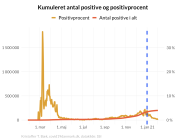
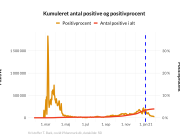
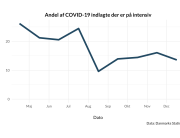
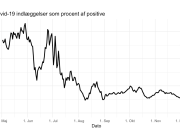
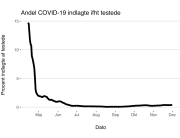
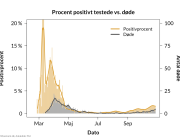
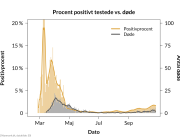
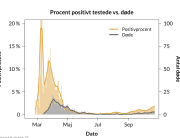
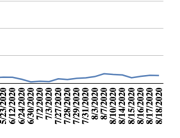
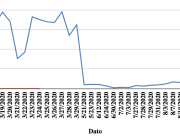
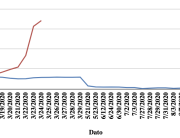
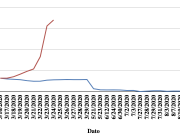
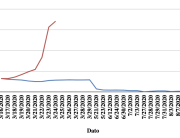
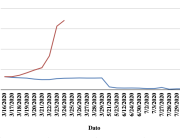
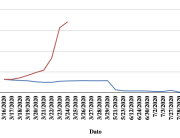
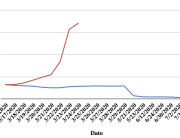
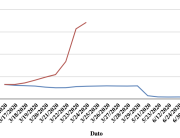
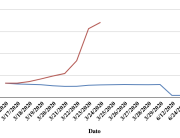
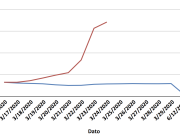
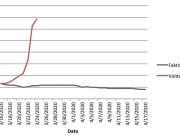
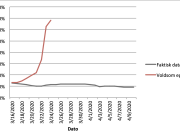
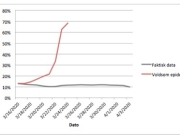
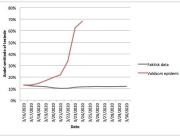
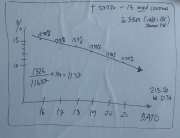
The research showed that in both Sweden and Denmark, the likelihood of experiencing side effects after Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine depended largely on which batch of the product the person received.
– “With this new study, we have been able to confirm a major safety issue with Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine. The Swedish data shows that this was not just a phenomenon in Denmark, as our earlier study has shown, but likely to be a widespread problem” says Dr. Vibeke Manniche, one of the researchers behind the study.
According to Dr. Manniche, such large differences in adverse event reports, related to specific batches of a medical products, would normally have led to safety reviews and product recalls.
In both countries Pfizer/BioNTech’s COVID-19 vaccine that was the main one used to vaccinate the population.
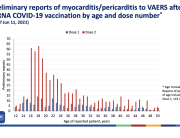
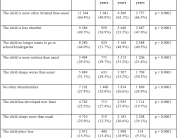
Analysis of Swedish data found that reports of side effects were distributed between batches of vaccine that showed in 3 very different side effect profiles. This reveals a safety issue identified in Denmark and confirmed in Sweden. The same pattern has also been reported in an independent study from the Czech Republic published in June 2024 (Fürst et al., 2024). This is highly irregular as a medical product should present a single side effect profile, not 3 different ones.
A second important aspect of this research is that the Swedish data shows a large degree of side effect underreporting, particularly from health professionals.
- “The purpose of an adverse event reporting system is in the early identification of side effects associated with a medical product, particularly serious side effects. In the case of BNT162b2 and other COVID-19 vaccines, for some reasons this did not happen, and safety signals were missed. Our findings show that the official reports reveal serious concerns about vaccine safety, which have not been properly addressed. Evidence suggests that the official data we were provided with has not been analysed for batch dependent safety signals” says Associate Professor Jonathan Gilthorpe.
As a third finding, this new study revealed that the large majority of reported side effects, some 75%, effected women.
- “There could be several reasons for such an observed gender difference. But whatever the reason, it is a safety signal that should have been scrutinised by the authorities”, says statistician Max Schmeling.
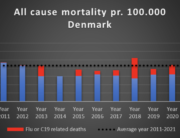
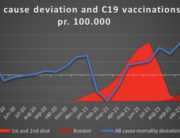
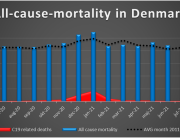
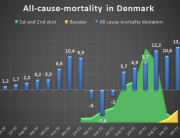
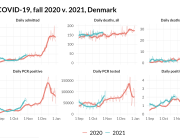
The researchers are now investigating the mortality associated with the COVID-19 vaccines and expect to publish their findings later this year.
Behind the research are statistician and economist Max Schmeling, Associate Professor Jonathan Gilthorpe, Professor Peter Riis Hansen and M.D.-Ph.D. Vibeke Manniche.
Link to the new study:
Reports of batch-dependent suspected adverse events of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine: Comparison of results from Denmark and Sweden.
https://www.mdpi.com/1648-9144/60/8/1343
Schmeling et al., 2023:
Batch-dependent safety of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/eci.13998
Fürst et al., 2024:
Batch-dependent safety of COVID-19 vaccines in the Czech Republic and comparison with data from Denmark https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/eci.14271
For further info:
Dr. Vibeke Manniche: Tel. +45 40312045 vibeke@vibekemanniche.dk